ECONOMIC PART
In the backyard garden, in the economic part, garbage bins should be located, a clothes horse and a place for compost. A place for the utility part should also be planned on the plot, of course, without the beater.
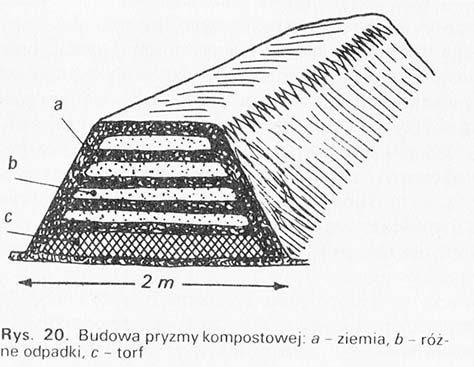
For the composting of various types of waste, coming from the garden, a place shaded by trees or tall plants is chosen, to keep the compost pile from drying out. If there is no such place in the garden, create an artificial cover on the south side, eastern or western with a roach or pergola, planted with climbing plants. A rectangle of width is marked on the selected place 1,5 m and a length of approx 2 m. From the place intended for the compost pile, the humus soil is removed to a depth 20 cm. You can use it later to cover the stack. Then a layer of peat or old compost is laid in this place, so that it absorbs and retains nutrients, washed away by rain from the compost pile.
In such a prepared place, loosely collected waste is placed, coming from the garden, like for example.: tree leaves, healthy haulm of tomatoes, beans, peas, pulled out weeds, bird fertilizer, wood ash. Such layers, if they are thick 20 cm, covered with humus soil or peat. When the stack reaches 1 m in height, it is covered with humus soil or peat, a trough-shaped depression is formed in it, that rainwater does not run off, and pierces a few holes with a pole all the way to the base of the stack, to facilitate the penetration of water inside.
To ensure a quick and even decomposition of the organic substance accumulated in it throughout the pile, adequate humidity must be maintained, sprinkling it with water as needed. In order to speed up this decomposition, the stack must be turned over, and it is this way, to keep the bottom and middle layers of the compost material on the outside and on top. After the pile has been flipped over, it is poured over with water. The more times it is done (not more often than every two months), the faster you get "mature"” compost. To prevent the stack from freezing, it should be placed a little higher during the last pre-winter transfer of the compost – do 1,5-1,8 m – and cover with plant haulms or leaves. This allows for further fermentation and maturation of the compost even in more severe frosts. After one year of fermentation, the compost should be suitable for fertilization (it is then dark in color).
The fertilizing value of composts depends on the material and the method of their preparation. On average along with 100 kg of compost is added to the soil: 0,3 kg azotu, 0,2 kg of phosphorus and 0,2 kg of potassium and trace elements. The compost should usually be given twice as much as the manure, i.e.. at least 600 kg in 100 m2. The laying of the compost heap is shown in the figure.