Asparagus
Asparagus
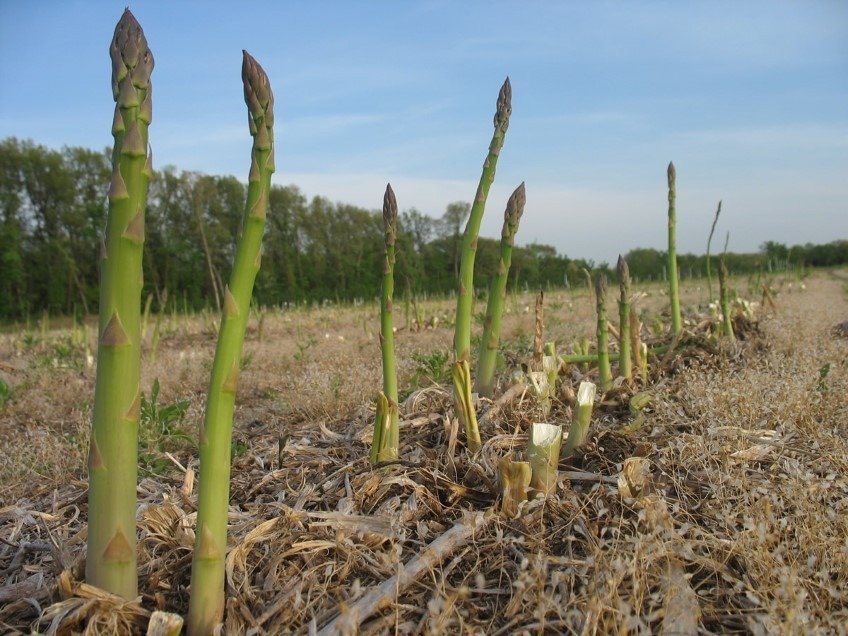
Asparagus is one of the earliest field vegetables. The edible part is the shoots growing from the rhizomes (so-called carp), called projections. Usually bleached shoots are eaten (shoots covered with earth – White), but more and more often, unbleached asparagus is recommended, green, which are more nutritionally valuable. Asparagus has a high biological value due to the high content of B vitamins and chemical compounds regulating the water balance in the human body.
Asparagus has high heat requirements, especially during the period of the formation of the tabs, therefore it should be planted in a sunny place, sheltered from the winds. Asparagus hates acidic soils, which should be limed before planting carp. It grows best in fertile soil, airy, and because it is rooted very deeply, the soil may be dry. The best are sandy loam, with high humus content. The soil crust causes the curvature of the protruding protrusions.
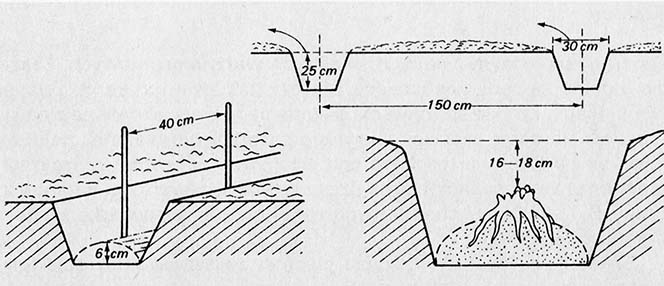
Asparagus can be propagated from seed, while preparing the carps for planting. We sow the seeds in early spring on the seedbed, in rows what 40 cm. The depth of the seed cover – 3-4 cm. On 1 m2 is sown 1,2-1,5 g nasion. In order to shorten the germination period, the seeds are soaked through 3 days in water at 25-30 ° C, and then dry and sow. The seedlings are interrupted, leaving them making 15 cm. To get a well-grown seedling, it is recommended to sow seeds for inspection in mid-March (with 1 g of seeds are obtained approx 30 plants) and quilt on the seedbed. Plants are fertilized with nitrate in a dose 20 g / m2 and again at the end of July in the dose 10 g/m2. In autumn, dead shoots are cut and burned, to prevent the development of pests, and covers the seedbed with straw fertilizer for the winter, with peat or leaves. In the spring of the following year, young plants are dug up, chooses well-developed stumps and plantes them permanently. This place is fertilized with manure in the fall (4-6 kg/m2) and mineral fertilizers in quantity 15 g superfosfatu i 30 g 40% potassium salt per 1 m2. Asparagus is planted at a distance of 120-150X40-50 cm (with a small number of plants – spaced 100X100 cm), in the pits in depth 20-30 cm. At their bottom, asparagus roots are spread, and then covered with a layer of earth to a thickness of 16-18 cm. The wells fill gradually, as the plants grow in the first year of vegetation.
In the first and second years after planting, the plants are fed with ammonium nitrate 2-, 3-fold, using each time after 20 dag of ammonium nitrate per 10 m2. Fertilization is applied for the first time after breaking the green shoots, and then at intervals 4-, 6-weekly. Concentration of Florovit can also be used for top dressing 1%, using after approx 2-3 And the solution on the plant. In the fall, we feed the asparagus with potassium salt (25 g/m2) i superfosfatem (15 g/m2). In the fall, cut dry shoots and burn them. Places, where the plants died, we mean, to replant them in spring. In the first year after planting the asparagus, other vegetables can be grown in the row between rows. In the second year of cultivation, independent of nitrogen fertilization, we feed the asparagus in the spring as follows: 40 g 40% potassium salt, 30 g of superphosphate on 1 m2. We can only collect tabs in the third year. If we want to whiten them, we form it above the planted plants (space is significant due to cut shoots) wide shafts at the base 40 cm, in the following years, increasing the width to 50-60 cm. The height of the shaft should be 25-30 cm. So that the earth does not crumble, the shafts should be semicircular in shape. With only a few plants, mounds are formed above them.
Harvesting begins when you notice the first peaks of protrusions above the ground or cracks in the embankment or mounds. Then the soil is removed in this place with a hand or a hoe and the tab is broken off or cut with a knife (there are knives designed for this purpose, resembling a chisel with a wider blade) next to the carp. The soil is then scraped back up and tapped together. Unbleached tabs are cut as low as possible, slightly below the ground. In the following years, the collection lasts from May through 7 weeks, i.e.. do 15-20 June. The highest yields are obtained between 5 a 10 a year after planting the asparagus. WITH 1 m2 is obtained approx 0,25-0,5 kg of tabs. After harvesting, the dikes or mounds should be spread, to allow green shoots to grow properly.
Three varieties are grown:
Limbras F, – early variety, very fertile. The tabs grow out thick, heads compact.
Mary Washington – medium early, fertile. Thick, large tabs, compact heads.
Schwetzingen master shot – mid-early variety, very fertile. Thick tabs, aligned, strict heads.