 MULTIPLICATION
MULTIPLICATION
Most fruit plants reproduce vegetatively – by detaching or transferring to the rootstock the vegetative organs of the mother plant. The exceptions are wild strawberries and walnuts, which so far reproduces most often from seed. From seeds it is impossible to propagate noble fruit trees and berry plants, because most often "wild boars" will grow from the seeds” about small fruits, unpalatable, unlike the fruits of their "parents."”. Therefore, in order to consolidate the characteristics of noble varieties, we must resort to vegetative reproduction. Strawberries reproduce naturally, by runners, the so-called. mustache, raspberries – by root suckers, which can be separated from the mother bush. Currants and gooseberries are propagated by woody cuttings or layering.
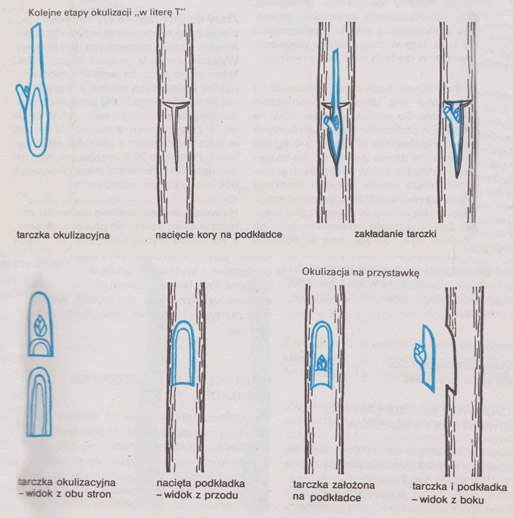
Fruit trees are propagated by eyelets or grafting noble varieties on rootstocks (popularly known as wild boars), in the past, most often obtained from sowing. Nurseries do it, which must be driven (in accordance with the Nursery Act) special permission. In the chapter entitled. Nursery material, the production of fruit trees is discussed, as a reminder, a few sentences about the rootstocks.
The rootstocks used for individual species of fruit trees are given in the subsection entitled. Selection of varieties. Generative rootstocks are obtained from seeds collected from certified mother trees, proven in terms of health and resistance to frost. As a rule, a common feature of all generative rootstocks is a high growth force, which they pass on to the cultivars which have been vaccinated or grafted on them. For this reason, they are called vigorous rootstocks, and the trees obtained on these rootstocks – vigorously growing trees. Such trees should not be planted in small gardens and allotments, because I take up too much space. Pads (all clones, that is, the types of reproduction) vegetative ones are most often obtained by the method of vertical or horizontal depositions, in specially established nurseries. They are therefore clones that are an extension of the line of one, previously selected, a copy – hence their names or numbers. The advantage of all vegetative rootstocks is this, that they have genetically stabilized traits, especially the strength of growth and resistance to frost. Vegetative rootstocks – depending on the characteristics of the plants, from which they were selected, or from which they arose as a result of crossing - they show differentiated growth force and a correspondingly different influence on the growth of a given cultivar. On this basis, they are divided into: dwarf – strongly weakening growth, semi-dwarf – moderately weakening growth and strongly growing – not weakening growth. Only dwarf trees are recommended for small gardens and allotments, which form small crowns and begin bearing fruit early.
In each fruit tree it stands out 3 basic parts: root system, trunk and crown.
The root system is most often of the bundle type, though in some species (cherry, pear tree, Walnut) a distinct tap root is marked, as a result, these trees cannot be planted in areas with shallow groundwater levels. Cherries also hate the high level of groundwater, apple trees, apricots and even plums.
The trunk is a straight section of shoot between the root collar, and the base of the lowest skeletal shoot of the crown. Its height does not depend on the type of washer – both on dwarfs, and vigorously growing trees can be obtained (pienne, bushy).
The crown consists of a guide, which is usually vertically growing, the strongest shoot in the crown and skeletal shoots departing from it (First row), semi-skeleton (II and further rows). In older fruit trees, skeletal shoots are usually called branches, and semi-skeletal – branches. Both long shoots and short shoots grow from boughs and branches of different rows, on which leaf and flower buds or mixed.
Fruit trees, depending on the height of the trunk, divided (in accordance with applicable standards) and: bushy (K) – trees with no trunk at all or with a trunk not exceeding height 30 cm, low foaming (E.G) – about the height of the trunk from 31 do 60 cm, half-foams (PP) – about the height of the trunk from 61 do 100 cm i pienne (P) – about the height of the trunk above 100 cm.
