ELEMENTS OF GARDEN ARCHITECTURE
The backyard, which performs multiple functions, it is also a setting for a residential house or an element of urban green areas, where people are looking for rest and entertainment. Therefore, an important role, both for the overall aesthetics of the garden, as well as convenience, and sometimes the entertainment of the user of the resort, meets the so-called. garden architecture. Plants are a plastic complement to this architecture and discreetly mask the objects, which often do not want to be revealed to the viewer, while other objects emphasize.
Fence
The fence is one of the most important elements of garden architecture. In employee allotment gardens, the regulations only allow fencing for the entire set of plots, made of the same material with a height 1 m, only with the consent of the garden management (which was about before). So it is usually a garden alley fence. They are made of a net that is stretched on posts which are pieces of steel pipes planted in concrete. For a home garden, the most suitable fence will be a mesh with steel frames on the foundation.
It is not recommended to use a hedge in allotment gardens. However, the hedges form an aesthetic border around the plots, however, maintaining them is quite troublesome. The hedge requires pruning several times a year; not sheared instead of adornment, disfigures the plot. In addition, the plot is slightly shaded by the hedge, depriving the adjacent strip of land of food and water. Despite these disadvantages, it is worth using in home gardens, especially when it separates the garden from the street, acting as a cover, and at the same time insulation against dust and fumes. The best plants for low hedges are: common liguster (Ligustrum vulgare), alpine currant (Ribes alpinum), glossy cotoneaster (Cotoneaster lucida), pink snowball (Symphoricarpus orbiculatus), pigwa japońska (Cydonia japonica). It is used for tall hedges: grab (Carpinus betulus), field maple (country maple), Siberian Caragan (Caragana arborescens), mulberry (White mulberry), cherry plum (Prunus africana) or regret (Prunus divaricata) or an anti-locker (Prunus mahaleb). Decorative, but conifer hedges are difficult to maintain and very expensive, such as: thuja (Thuja), pea cypress (Chamaecyparis pisifera) i cis (Taxus baccata).
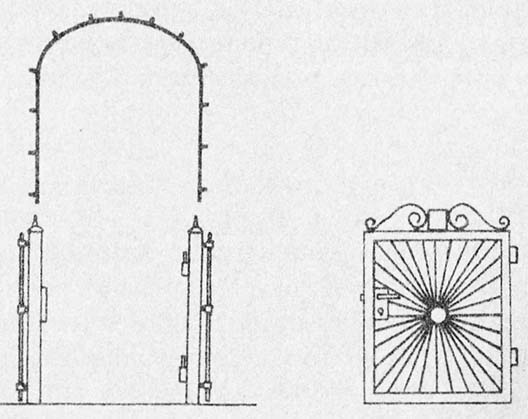 A gate is a component of the fence, which can be a nice decoration. The figure shows the goal made by Bogdan Dubek, a plotter from Elbląg (it is made of an angle bar, grade. St. 3525X25X25X3, rods with a diameter 10 i 12 mm and galvanized sheet, type. St.OS-0,5 Mm).
A gate is a component of the fence, which can be a nice decoration. The figure shows the goal made by Bogdan Dubek, a plotter from Elbląg (it is made of an angle bar, grade. St. 3525X25X25X3, rods with a diameter 10 i 12 mm and galvanized sheet, type. St.OS-0,5 Mm).
Retaining and flower walls
Retaining walls and flower walls are built on a terrain diversified in terms of height. A distinction is made here between the actual retaining walls (lity mur), made using the construction method, and the so-called. flower walls, dry laid out of stone, that is, using soil in place of mortar, or partially bonded with cement mortar, with slots filled with earth, in which we plant rock plants. For the construction of proper retaining walls, a foundation must be made, reaching the freezing point (100-120 cm). The walls are made of stone, concrete or clinker. At heights above 1 m, the wall thickness should be calculated by a construction specialist. For flower walls – depending on the height, a shallow foundation is used (20-30 cm at walls to 80 cm in height; do 50 cm at higher – 120-150 cm). In areas with high groundwater levels or on a slope, when there is a risk of being washed away, drainage of the "footing" should be used”. For this purpose, a layer of debris is poured or drainage filters are installed.
The wall thickness depends on the height. At the height 80-100 cm thickness should be 20-30 cm. The wall can be made of stone of various shapes and origins, and even concrete scrap, who gladly sell home factories. The easiest way is to build a wall made of large stones. We use a rope to keep the line even, and fill the gaps with smaller stones. In the case of building higher walls, it is necessary, to reduce the earth pressure, tilt the low wall from the vertical by at least 7-8 cm and 1 m in height, towards the higher ground. The gaps between the stones should not be on one line. At intervals, longer stones are placed to connect the wall with the back. In order to strengthen the structure, the wall can be partially bound with cement mortar. Similarly to mortar, the gaps between the stones are filled with a mixture of humus soil (preferably compost, clay and peat). The closest vicinity of the wall is also filled with such a mixture, to allow plants to be planted there. In order to irrigate the substrate for plants, cement or stoneware pipes with little light are placed, delving them into 1/3 – 2/3 the depth of the wall. Through these pipes it will be possible to water deeper layers of the earth.
